Table of Contents
What is Letter of Credit?
A Letter of Credit (L/C) or Documentary Credit refers to a contract/ agreement/ undertaking to facilitates the guaranteed payment mechanism to the exporters of goods or services by the banks on the behalf of importer/ buyer provided the supplier fulfill all the predefined conditions described in the sale contract between supplier and buyer.
The Letter of Credit (L/C) is regulated under the UCPDC (Uniform Customs and Practice for Documentary Credit) 600 Act 2007 established by the ICC (International Chamber of Commerce), generally used to facilitate international trade where the creditworthiness of buyers or suppliers is difficult to judge.
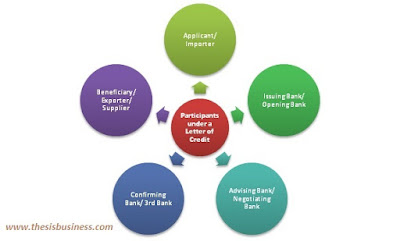
Participants under a Letter of Credit:
There are following participants which are essential to establish a letter of credit or documentary credit.
The applicant is also known as buyer or importer refers to those who are willing to purchase some goods or services and approaches to his bank to issue a credit letter.
2) Issuing Bank:
This bank mostly exists in buyer’s locality also known as Opening Bank which initiates the LC on the importer’s request. In other words, the bank which is accountable to make payment for the supplied goods or services on the behalf of the applicant (buyer).
3) Advising Bank:
This bank is also known as Negotiating Bank which exists in the supplier’s locality. This bank is responsible to make payments to the exporter/ supplier on successful completion of shipment of goods or services.
4) Confirming Bank:
This is also known as additional banks which also resides in the supplier’s locale. It is an optional bank generally appointed on the recommendation of the supplier to build the confidence of exporter regarding the payment assurance.
5) Beneficiary:
A beneficiary is a supplier or exporter itself. The supplier may be the manufacturers or traders of goods or services.
Process of Letter of Credit:
The mechanism/ process of the letter of credit is explained step by step below.
Step 1: The buyer/ importer/ applicant propose supplier/ exporter to purchase certain goods or services on a specific date, price and specific quantity. The supplier agrees and both sign a sale contract in which all conditions are well notified.
Step 2: The buyer approaches his bank and asks to issue a letter of credit regarding the sale contract signed with the supplier. The Issuing Bank verify the documents and credentials of the buyer and forward to the Advisory Bank that is situated in the supplier locale.
Step 3: The Advisory Bank receives the documents and contacts the supplier to confirm whether the sale contract is genuine or not. If the supplier confirms and agrees with the respective contract then a letter of credit is established.
Step 4: If the supplier/ beneficiary wants the guarantee of any other bank as well, then the third bank knows as confirming banks involves under the letter of credit (L/C).
Now an LC is established and all the parties are under the UCPDC 600 Act. They will have to follow the guidelines of the UCPDC Act.
Step 5: Now after the certain time as per documented in sale contract exporter manufacturers the goods and shipped it to the buyer through any freight forwarders. The date on which the goods are shipped is known as Date of Shipment.
Step 6: The beneficiary submit all the necessary documents related to shipment and exported product to Advisory Bank.
Step 7: The advisory bank examines all the documents within 5 banking days and transfers payment to the beneficiary account if each document is all right.
Step 8: Now advisory bank forward same document to issuing bank. The issuing bank also examines all documents and further transfer the amount to the advisory bank within 5 banking days.
Step 9: The issuing bank may receive the payment from the buyer in three ways:
- Advance or loan
- Bill of exchange (On-site or Usance)
- Full advance payment
Thus the cycle of letter of credit is now completed.
Letter of credit Example:
Keep the above steps in mind to understand the concept of the letter of credit more clearly. The letter of credit is mostly used in international trade (Exports and Import) because the seller and buyer are unknown to each other and separated by distance. In case of any dispute, it would be troublesome for the exporter as well as importer.
Suppose there are two parties A (India) and XYZ Ltd (USA). Mr A wanted to purchase 5 pieces of MRI machine ( worth Rs 25 Crore) for his diagnostic centre but he doesn’t know anything about the company XYZ ltd which is the manufacturer of MRI machines.
- Mr A contacted a company XYZ Ltd and sign a sale contract of 5 MRI machines with the company. But here is a problem neither A will make payment first nor the company will manufacture the machines first.
Therefore the solution is to deal with the letter of credit (L/C).
- Hence Mr A will contract the HDFC Bank and ask to issue the L/C with the payment of Rs 25 Crore.
- HDFC Bank will approach the City Bank in the United States and Forward the necessary documents for confirmation of sale contract from the manufacturer (XYZ ltd).
- On the confirmation of the manufacturer, the letter of credit is established and all four participants bound with a contract.
- After a certain predefined date, XYZ ltd manufactured all 5 machines and shipped. Now the company submit all the necessary documents to the city bank for remittance of the payment.
- City bank transfers the amount 25 Crore to the company’s account and claims this amount from Hdfc bank.
- Hdfc bank settles the payment of city bank and further collect the payment from Mr A.
Documents in Letter of Credit:
Following are the documents required to receive payment in a letter of credit.
- Bill of exchange
- Invoice (exported product or services)
- Shipment or transportation document (Example- Bill of lading or Airways Bill or Railways Receipt or Bilty)
- License regarding the product (if applicable)
- Government associated document (Certificate of origin, Embassy legal certificates etc)
- Insurance Certificate
- Guarantee or warranty certificates
Hope you would have got sufficient information regarding the Letter of Credit (LC). Thus we understood the significance of an LC in foreign trade (Export-Import Business). Thus a letter of credit facilitates international trade and provide a guaranteed payment process between traders.
You may also interested in the following topics.
What is Hedging in Finance?
What are Factoring and Forfaiting Services?
What are Factoring and Forfaiting Services?