Every corporation whether it is emerging or establish, require funds at some stage during its operation and raise capital from the financial market is the most popular and convenient mode of arranging finance. Hence, the business corporates raise from the market by issuing financial securities and on the other hand individuals or institutional investors purchase these securities to invest their money to earn a profit.
Thus the role of merchant banks emerges in such circumstances. In this topic, we will learn the concept of Merchant Banking in brief.
Table of Contents
Merchant Banking –
“Merchant Banking refers to the financial intermediary services provided by specialised banks called Merchant Bank (other than commercial banks) for business corporates and individual with high net worth.”
Merchant banks act as an intermediary/ middleman between business corporates and investors. In other words, merchant banking is financial intermediation between the business entities which require funds and the investors who possess ready capital and seeking an opportunity for investment so that they can make a return.
Thus we can say that Merchant banking matches the gap between the issuer of capital (Corporates) and purchaser of capital (Investors). Hence, it is the function that facilitates the flow of capital in the financial system.
Role of Merchant Banking –
- Merchant Banking facilitates in channelising the financial surplus of the general public into productive investment avenues.
- It coordinates the activities of various intermediaries to share issue.
- It ensures compliance with rules and regulations governing the securities market.
- Merchant banking is said to be the centre of capital market operations and their activities are primarily non-fund based.
- Their basic requirement is a high professional with skills and worldwide contact.
Merchant Banking – Origin
The concept of merchant banking is originated in the 13th century in Italy and the first-ever merchant banks were Riccardi of Luca, Medici, Fugger etc. Initially, there was no distinction between the functions of commercial banking and merchant banking until 1932.
The merchant banks are also known as “Accepting and Issuing Houses” in the United Kingdom and they are known as Investment Banks in the United States as well.
Merchant Banking in India –
Merchant Banking Service in India was originated in 1969 when the merchant banking division of Grindlays Bank was initiated for undertaking and management of the public issue and financial consultancy. Further, the State Bank of India started merchant banking service in 1973 and ICICI Bank Ltd became the first development financial institution to initiate merchant banking services in 1974.
During the mid-seventies, India witnessed a boom in the growth of merchant banking organisations that were sponsored by the banks, NBFCs, Brokers etc. This led to the diversification into the scope of the following activities.
- Loan Syndication
- Portfolio Management
- Corporate Counselling
- Project Counselling
- Debenture Trusteeship
- Mergers and Acquisitions
However, the scope of such services was neither defined nor any rules and regulations were set up to govern such activities. Then in 1992, the formation of SEBI (Securities of Exchange Board of India) was taken place. This became a landmark in the evolution of merchant banking as a professional service in the country.
Merchant Banker Functions –
Although merchant banks provide numerous services to their client these days, some of the most significant functions of merchant banks are explained below.
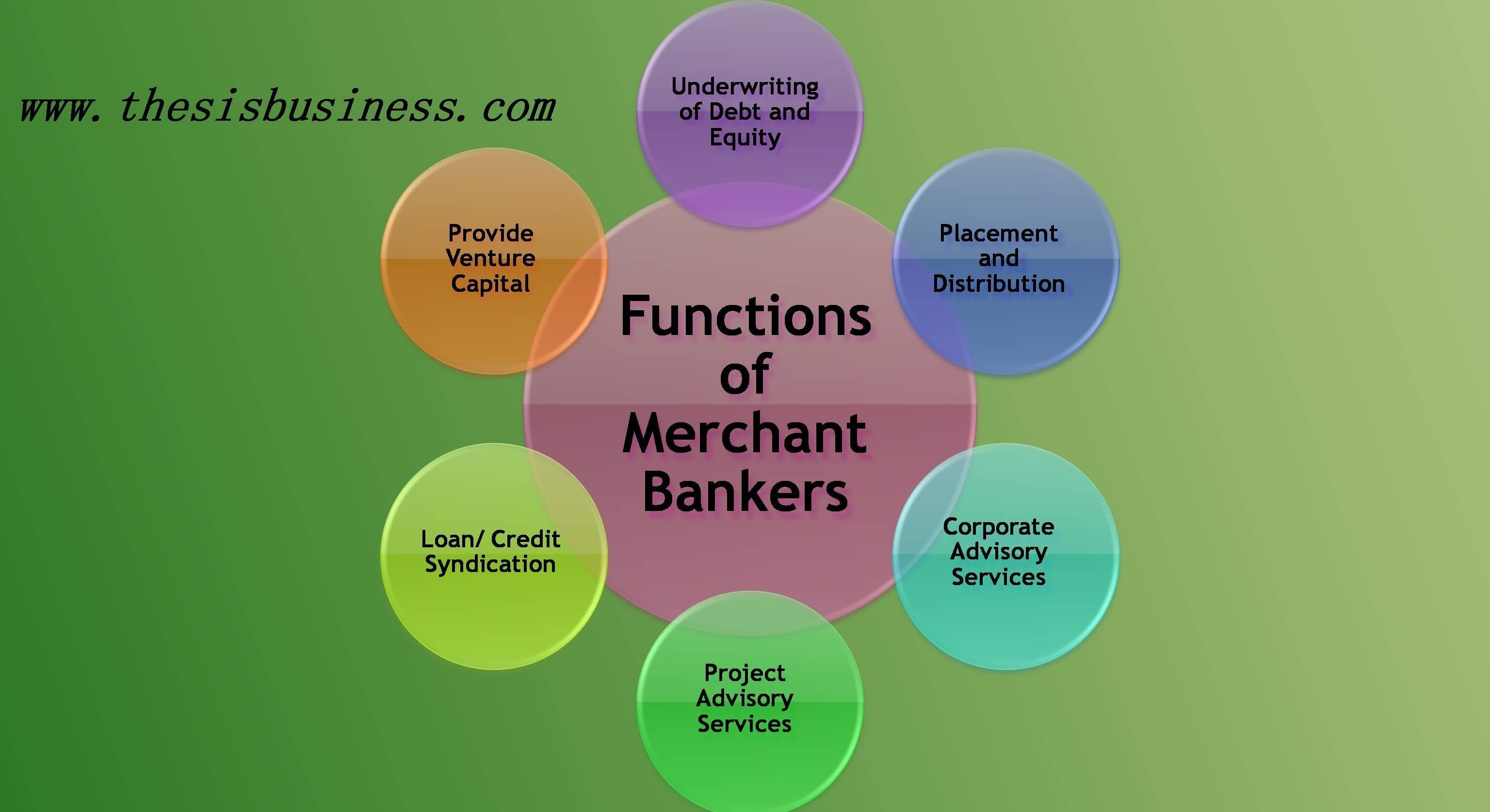
1) Underwriting of Debt and Equity –
Underwriting/ management of debt securities such as debentures and share capital is one of the most important functions of a merchant banker. The merchant banks act as middlemen between the issuer of debt securities and individual or institutional investors and assists the companies in raising funds from the market. Merchant banks evaluate the value of the business and the number of shares or debentures is to be issued.
2) Placement and Distribution –
The merchant bankers facilitate in distributing various securities like equity shares, debt instruments, mutual funds, fixed deposits, insurance policies, commercial papers and distribution network of the merchant banker can be classified as institutional and retail.
3) Corporate Advisory Services –
Merchant bankers offer customised solutions to their client’s financial problems and financial structuring includes determining the right debt-equity ratio and gearing ratio for the client and appropriate capital structure theory is framed as well.
Merchant banker explores the refinancing alternatives for the client and evaluates cheaper sources of funds. It also provides Rehabilitation, Turnaround and Risk management services such as designing a revival package in coordination with banks and financial institutions for sick industrial units, appropriate hedging strategies to reduce the risk associated.
4) Project Advisory Services –
Merchant bankers help their clients in various stages of the project undertaken by the clients:
- They assist them in conceptualising the project idea in the initial stage
- Once the idea is formed, they conduct feasibility studies to examine the viability of the proposed project
- They also assist the client in preparing different documents like a detailed project report
5) Loan/ Credit Syndication –
Merchant bankers arrange tie-up loans for their clients. This takes place in a series of steps. Firstly they analyse the pattern of the client’s cash flows, based on which the terms of borrowings can be defined. Then the merchant banker prepares a detailed loan memorandum, which is circulated to various banks and financial institutions and they are invited to participate in the syndicate. The banks then negotiate the terms of lending based on which the final allocation is done.
6) Provide Venture Capital and Mezzanine Financing –
Merchant bankers help companies in obtaining venture capital financing for financing their new and innovative strategies. They also help small organisations and entrepreneurs to obtain initial funding, other business ideas and opportunities, Government policies and incentives.
In addition, merchant bankers also provide various other services as well.
7) Portfolio Management Services –
Merchant banks offer portfolio management services to their clients. They guide their clients regarding profitable, easy liquid and less risky investment avenues. They also update their clients with important and crucial news and updates regarding investment opportunities and market fluctuations.
8) Interest/ Dividend Management –
Merchant bankers also facilitate their clients on computing, declaration and allocation of interest on debt securities such as debentures and dividend of shares/stocks.
9) Brokerage Services –
Merchant banks also act as a broker in the stock exchange. They purchase or sell the shares on behalf of their clients and also provide guidance on which or when to buy or sell shares.
10) Manage Money Market Instruments –
Merchant bankers also manage money market instruments like Government bonds, Treasury bills, commercial papers, certificates of deposits for Government entities as well as large companies and financial institutions.
Registration of Merchant Bankers –
To function as a merchant banker, a business firm or company needs to register with SEBI and comply with the following terms and conditions:
- The applicant should be a body corporate and should have a minimum net worth of Rs.5 crores.
- The applicant should not carry on any business other than those connected with the securities market
- The applicant should have the necessary infrastructure like office space, equipment, manpower etc
- The applicant must have at least two employees with prior experience in merchant banking
- Any associate company, group company, subsidiary or the interconnected company of the applicant should not have been a registered merchant banker.
- The applicant should not have been involved in any securities scam or proved guilt for any offer.
Conclusion –
Hope the article would able to elaborate on the complete overview of merchant banking. Merchant bankers establish a bridge between demand and supply of capital in the economy. The merchant bankers also arrange the capital for the organisations which are unable to raise funds from the public through private placement.
References: Wikipedia
