Table of Contents
What is Monetary Policy?
 |
| www.thesisbusiness.com |
“The Monetary Policy is the sets of policies (rules and regulations or activities) which are adopted by the Monetary Authority (central bank) of a country to regulate the money supply, to influence inflation rate, interest rates, unemployment rate and to stabilise the currency exchange rate with respect to other currencies.”
In simple words, the Monetary Policy is the guidelines that are utilised by the central bank for the economic growth of a country as well as for maintaining the inflation rate.
The central bank such as Reserve Bank of India (in the case of India) is responsible to implement its monetary policy across the country. The central bank, being a monetary authority or the Statutory Body manages the supply of money and primarily focus on interest rates of short term credits through various instruments or tools such as Open Market Operations, Policy Rates and Cash Reserves Requirements.
Types of Monetary Policy:
Monetary Policy basically can be defined of two types depending upon the economic conditions of a country. The central bank increases the supply of funds in the market to promote the economic growth of a country, on the other hand, it restricts the supply of money to control the rate of inflation.
If the central bank uses the policy to encourage the economic growth of the country, it is known
as Expansionary Monetary Policy whereas if it implements those policies to control inflation rate it would be known as Contractionary Monetary Policy.
In other words, the sets of policies that promote the economic development of the country are called Expansionary Monetary Policy, on the other hand, the policies which are used to control inflation is called Contractionary Monetary Policy.
Instruments (Tools) of Monetary Policy:
Although various tools are used to implement the monetary policy by the central banks in different countries throughout the world yet there are three major instruments or tools which are used by every central bank to implement its monetary policy across their respective countries.
First one is Open Market Operations (OMO), in which the central bank purchases and sells the government bonds and other approved securities to the commercial banks to manage the supply of money in the economy.
The second one is Liquidity Adjustments Facility, under which the central banks issue the guidelines regarding Ratio Requirements for all commercial banks and other financial institutions such as Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) and Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR).
The third one is Policy Rates, in this tool the central bank determines the interest rates on very short term (one day or overnight) borrowing or lending for the commercial banks. There are various types of policy rates such as Repo rate, Reverse Repo rate, Term Repo or auction Repo, Bank rate for rediscounting of bills or commercial papers.
The central bank adjusts these policy rates to control the flow of liquidity to the banks and other financial institutions. A fluctuation in these rates directly affects the lending or borrowing interest rates in the market, hence availability of creditable funds can be influenced by adjusting the policy rates.
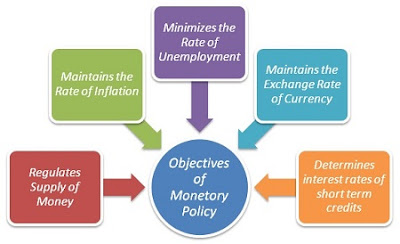
Objectives of Monetary Policy:
 |
| www.thesisbusiness.com |
Each central bank of a country produces its monetary policy to meet majorly three objectives.
- The first one is to promote the economic development of the country by pushing more funds in the economy ie. to increase the supply of money in the market. This leads to excess money available for commercial banks to provide various loans to their customers. Thus more money in the hand of people increases the inflation rate, which ultimately tends to increase the prices of goods and services. Thus it leads to the economic growth of the country.
- The second one is to control the rate of inflation, the primary objectives of any central bank are to maintain a healthy inflation rate beside of economic growth of the country. Though the objective of the central bank’s monetary policy to facilitate the economic development of the country however at the same time it ends rise in inflation rate as well. Therefore, monetary policy stimulates economic growth in such a way that the inflation rate should also be maintained in the country.
- The third one is to control the unemployment rate across the country, the central bank is also responsible for controlling the unemployment rate by utilising its monetary policy beside of inflation rate and economic development of the country.
Related Terms: