There are various types of bank accounts which anyone can open in nearby banks whether it is public or private. Are you a professional, self-employed or entrepreneur? Looking for opening a bank account or just curious to know the different types of bank accounts.
Probably, you would be preparing for Government exams and looking for comprehensive information regarding types of bank accounts in India.
Hence, in this article, let’s discuss different types of bank accounts which can be opened by anyone according to his requirements whether he is an individual or business entity.
Table of Contents
Different Types of Bank Accounts:
The banks whether it is public or private invite the general public or businesses to get their bank account opened.
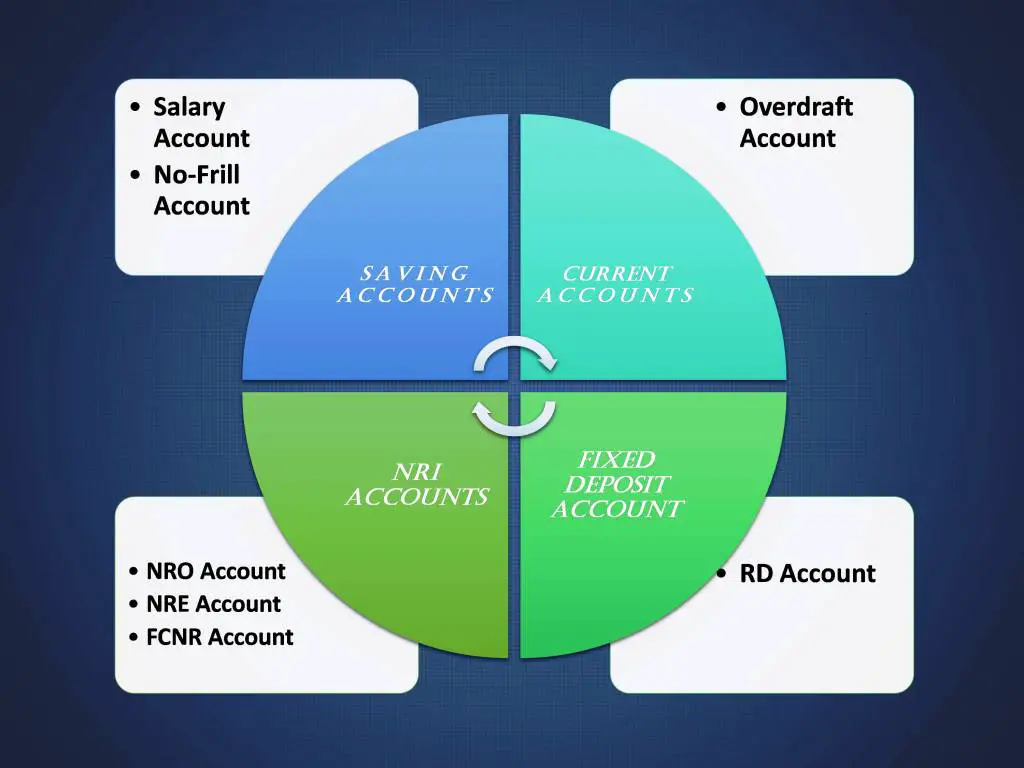
There are following types of bank accounts.
- Savings Accounts
- Salary Accounts
- No-Frill Zero Balance Accounts
- Current Accounts
- Recurring Deposit (RD) Accounts
- Fixed Deposit Accounts
- NRI Accounts
- Non-Resident Ordinary (NRO) Saving/ Fixed Deposit Accounts
- Non-Resident External (NRE) Saving/ Fixed Deposit Accounts
- Foreign Currency Non-Resident (FCNR) Accounts
Now let’s understand one by one the features and benefits of each account in brief.
1) Savings Accounts:
The savings accounts are the most common types of bank accounts which are opened by any individual for the purpose of enjoying the basic banking services. The savings account encourages the habit of saving money and the account holder is also entitled to earn interest against the money deposited in his account.
You can deposit any amount of money into your account as there are no restrictions on the number of deposits, however, there are restrictions on the number of free withdrawals (52 per year).
Moreover, there are some other specific types of saving accounts as well such as children accounts, women accounts, senior citizen accounts, family saving accounts etc.
The basic features of saving accounts are as follows.
- You will earn interest on the balance maintained into your account usually 3 to 4% per annum.
- You will get an ATM/ debit card associated with your account through which you withdraw money anytime.
- You can also get a cheque book for payment purposes to any party/ person.
- You will also be entitled to avail internet banking, mobile banking services by which you can transfer money to anybody using your phone/ laptop.
- You will also be notified for every transaction regarding your bank account through SMS and email.
However, you have to follow certain guidelines to use saving accounts.
- You will have to maintain a minimum account balance to avoid minimum balance charges.
- To avail cheque book you have some charges to the bank.
- You will have to pay the ATM charges annually to use ATM services.
2) Salary Accounts:
The salary account is a type of saving accounts which are opened on behalf of you by your employer whether it is government or private equity. The salary accounts are operated just like normal saving accounts.
Your monthly salary and reimbursement are credited into the salary account only. However, there are some additional benefits of holding a salary account. For instance, there isn’t such a criterion for maintaining a minimum balance amount.
To open a salary account, your employer provides you with a letter requesting to open a bank account (generally in the desired bank or any other). You need to present that letter into the local (said) bank and the bank will open your salary account within the stipulated time.
Sometimes, your employer itself opens a salary account on behalf of you as soon as you join the organisation.
3) No-Frill Zero Balance Accounts:
The No-Frill accounts were introduced for providing basic banking services and availing various government schemes like MGNREGA, Gas subsidy, KCC, pension, scholarships etc to the labour, farmers, women and students residing in villages and remote areas.
No-Frill Accounts can be open in any public or private bank or at the customer service point (CSP) of any bank with a minimum document (Aadhar card & passport size photo) only.
However, there are some limitations and advantages of using such accounts.
- You can’t withdraw the amount higher than 10,000/ at a time.
- Cheque book facility is not available.
- You don’t need to maintain a minimum account balance with such accounts.
- You will get a Debit/ RuPay card for withdrawal.
- SMS Notification Services is Available
- You can manage your account (money transfer, balance check, statement etc) through the mobile application.
4) Current Accounts:
The current accounts are typically opened and operated by the businesses, traders, cooperative societies and companies.
Such accounts facilitate the frequent cashless transactions between two parties during the sale and purchase of products/ services.
In the case of current accounts, there are no restrictions on the number of transactions per day and this is because these accounts are more convenient to the business people.
However, the account holders require to maintain a minimum balance amount criteria.
In addition, the services offered to the account holders are:
- Cheque book facility
- Internet/ mobile banking
- SMS Alerts
- ATM Service
- Overdraft facility (withdrawing surplus amount than what the balance available)
However, you don’t earn any interest on the amount deposited into the current accounts.
To open a current account you need to present the following documents.
- Proof of Registration of Firm
- Certificate of concern authority (Regarding business)
- PAN Card of the firm
- Proof of Identity and Address (Proprietor)
- Proof of address (Office/ shop)
5) Fixed Deposit Accounts:
Fixed deposit accounts are those wherein you need to deposit a lump sum (fixed) amount once for the fixed tenure and depositors will get a fixed rate of interest as well.
The money deposited is typically not allowed to withdraw till the maturity date, however, some banks offer premature withdrawal but they provide comparatively a lower interest rate.
The tenure of fixed deposit accounts varies from 7 days to 10 years and rates of interest are generally offered 6 to 7% depending on the banks. The senior citizens get an additional interest of 0.5% per Annum.
6) Recurring Deposit (RD) Accounts:
A recurring deposit account is such an account in which you are required to deposit a fixed sum of money periodically (every month or quarterly) for the stipulated tenure to earn a higher interest. The sum of money could be as low as Rs 50/ and tenure varies from 6 months to 10 years.
You can’t change the tenure and amount fixed in between otherwise a penalty shall be imposed.
In addition, you will earn an interest higher than a normal savings account and somewhere close to fixed deposits depending on how long you want to invest your money. However, senior citizens are rewarded for additional (generally 0.5%) interest rates.
Premature withdrawal is typically not allowed in case of RD accounts if done so a penalty (low rate of interest) shall be applicable.
7) NRI Accounts:
Apart from the above types of bank accounts, the banks also offer the accounts for other Indian people who are not residing in India ie Indian people living abroad.
Such accounts for Indian origin people residing overseas are called NRI (Non-Resident) Accounts. The NRI accounts can be both fixed or saving types of accounts.
The different types of bank accounts for non resident Indian are as follows.
a) Non-Resident Ordinary (NRO) Fixed or Saving Accounts:
The NRO accounts are simply savings or fixed accounts operated in Indian currency (Rupee) by the Non-resident Indian. Whenever an NRI deposits money, usually in foreign currencies, the funds automatically convert to Indian Rupee at the prevalent exchange rate.
The NRIs utilise such accounts to park their money in India. Besides, they can also pay their bills, instalments, and rent of foreign countries from NRO accounts.
The interest earned from the deposits in NRO accounts are taxable.
b) Non-Resident External (NRE) Savings/ Fixed Accounts:
The NRE accounts are similar to NRO accounts and money deposited to these accounts are converted to INR at prevailing exchange rates. Such accounts are used to park foreign earnings in India.
The NRE accounts are maintained in INR, however, the interest earned as well as principal amount both are transferable and exempted from taxes as well.
c) Foreign Currency Non-Resident (FCNR) Accounts:
The only difference between FCNR accounts and above two (NRO & NRE) is that FCNR is maintained in respective foreign currencies but NRO & NRE are maintained in INR.
However, the FCNR accounts are also exempt from taxes in India like NRE accounts.
Conclusion:
We have explained all popular and significant types of bank accounts which are operated with the commercial banks. Hope you would have understood all significant information regarding bank accounts operated by the Indian banks.
Related Articles:
What are Nostro, Vostro and Loro Accounts?
Escrow Account | How does it work?
Indian Banking System | Structure of banking in India
References: 1) HDFC Bank (source)
